TÜBİTAK 2209-A Research Support for Students of the Department of Mathematics!
The results of the 2024/1 term of the “2209-A – Research Project Support Program for Undergraduate Students,” conducted by TÜBİTAK’s ...

WAMS-I. Workshop on Applied Mathematics and Statistics
The Department of Mathematics at İzmir University of Economics is bringing young researchers together! I. Workshop on Applied Mathematics and Statistics, ...

The World Mathematics and Pi Day Event
World Mathematics and Pi Day has been celebrated with an event organized for the seventh time by the Department of Mathematics ...
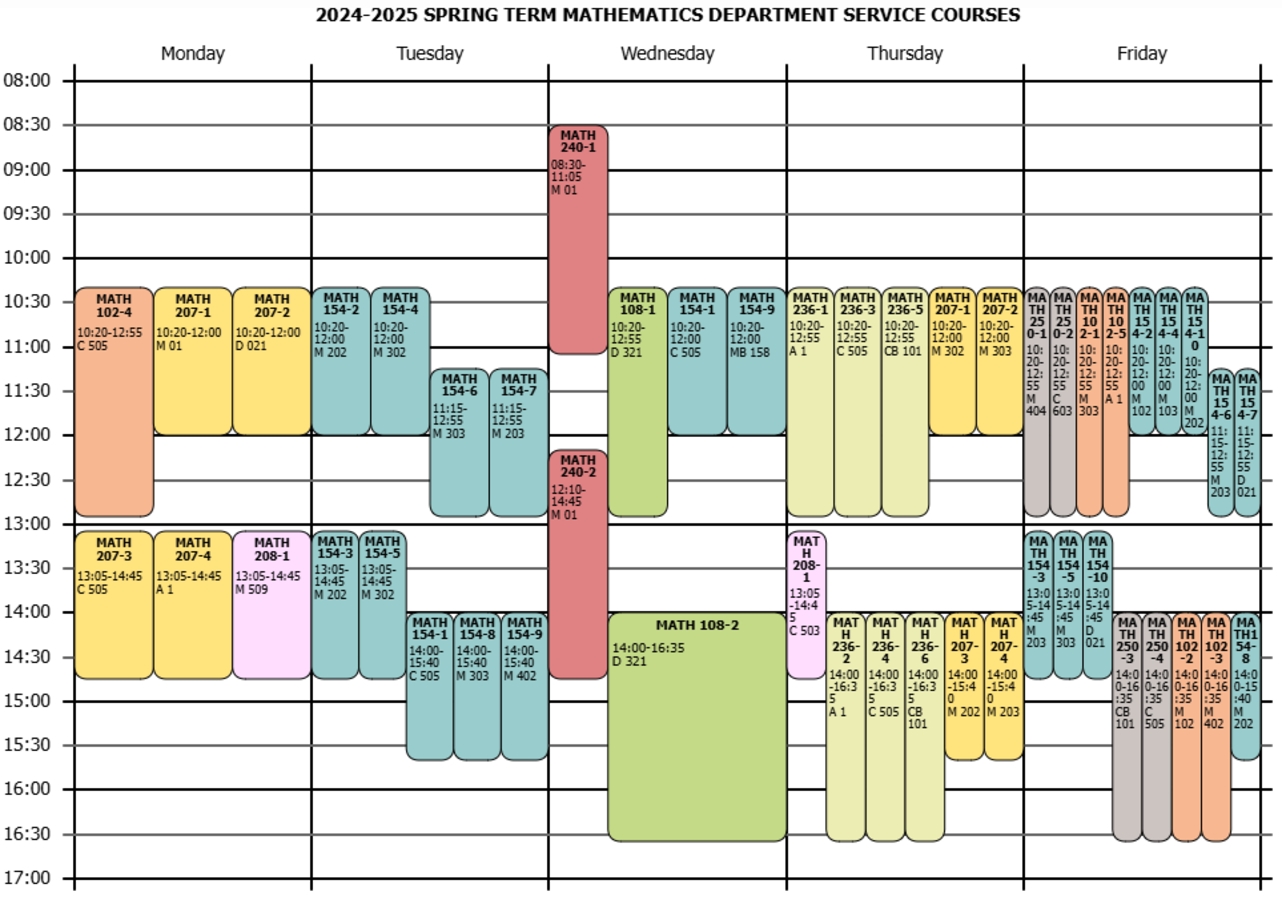
Service Courses Given by the Department of Mathematics
Service Courses Given by the Department of Mathematics ...

Prof. Dr. İsmihan Bayramoğlu participated in the "Forum of Azerbaijani Scientists Living Abroad"
Prof. Dr. İsmihan Bayramoğlu participated in the Forum of Azerbaijani Scientists Living Abroad, held in Baku from September 8-12, representing ...

"CSI Education 8th Season Teachers' Meeting"
Faculty members from our department, Vice Rector of our university Prof. Dr. Gözde Yazgı Tütüncü and Research Assistant Dr. Ayşe ...

9th Workshop of Association for Turkish Women in Maths Completed Successfully
As the Department of Mathematics, we hosted the ninth workshop of the Association of Women Mathematicians, whose mission is to ...

9th Workshop of Association for Turkish Women in Maths
9th Workshop of Association for Turkish Women in Maths will be hosted by our department between 03-05 May 2024. We have ...





