A Success Story from Our Graduate Pelin Erşin to LSE
Pelin Erşin, one of our 2024 graduates from the Department of Mathematics at İzmir University of Economics, has made us ...

Video-Supported Learning from IUE Department of Mathematics: Precalculus Recordings Completed
The Department of Mathematics at İzmir University of Economics has completed the video recordings for the Precalculus course, which covers ...

Outstanding Achievement in Poster Presentation by Our Student
Alican AKCA, an undergraduate student from the Department of Mathematics at İzmir University of Economics, has been awarded at the ...

I. Workshop on Applied Mathematics and Statistics Completed Successfully
The I. Workshop on Applied Mathematics and Statistics, organized by the Department of Mathematics at İzmir University of Economics, was held on ...

TÜBİTAK 2209-A Research Support for Students of the Department of Mathematics!
The results of the 2024/1 term of the “2209-A – Research Project Support Program for Undergraduate Students,” conducted by TÜBİTAK’s ...

WAMS-I. Workshop on Applied Mathematics and Statistics
The Department of Mathematics at İzmir University of Economics is bringing young researchers together! I. Workshop on Applied Mathematics and Statistics, ...

The World Mathematics and Pi Day Event
World Mathematics and Pi Day has been celebrated with an event organized for the seventh time by the Department of Mathematics ...
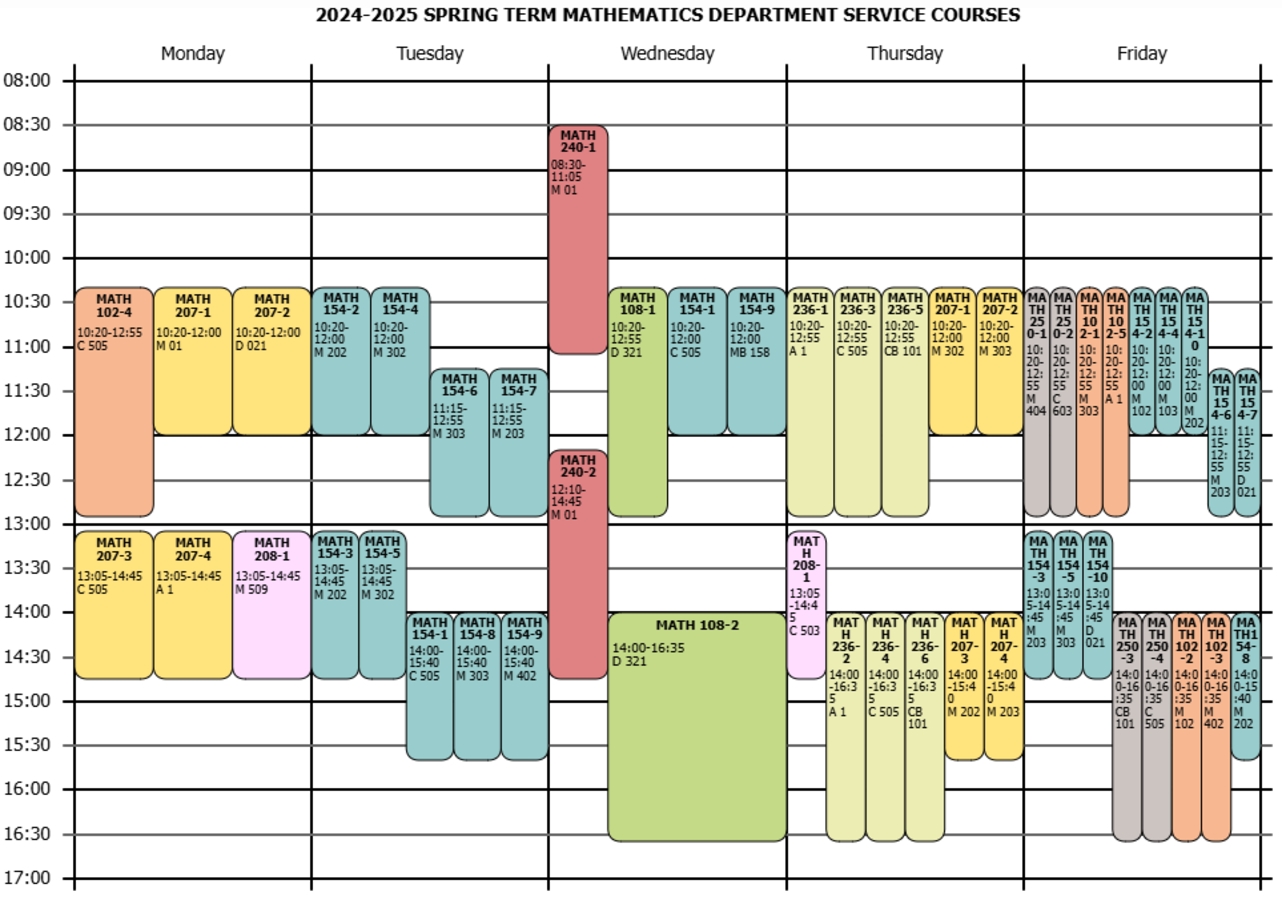
Service Courses Given by the Department of Mathematics
Service Courses Given by the Department of Mathematics ...





